Optic Neuropathy
Description
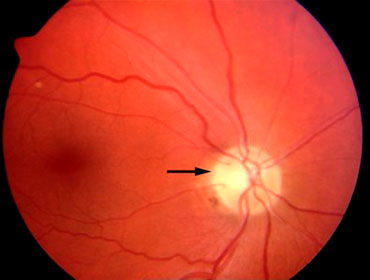
Demyelinating Optic Neuropathy (optic neuritis or retrobulbar neuritis) is an acute inflammatory process of the optic nerve, generally occurring in young adults. It manifests as an acute onset of visual loss, almost always unilateral.
The visual loss generally progresses over several days, remains stable for one to two weeks, and then gradually improves. The prognosis for recovery of vision is excellent with or without treatment.
Patients experiencing such conditions are encouraged to seek treatment, as the condition carries a high risk of subsequent development of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
Recent multicentre treatment trials indicate appropriate care within the first few days after onset are crucial.
While the application of intravenous steroid solutions does not alter the immediate visual prognosis, it does seem to retard the subsequent development of MS, over the next two years in patients for whom radiologic evidence suggests a higher risk of MS.